- Delhi, NCR
- +91-7840059590
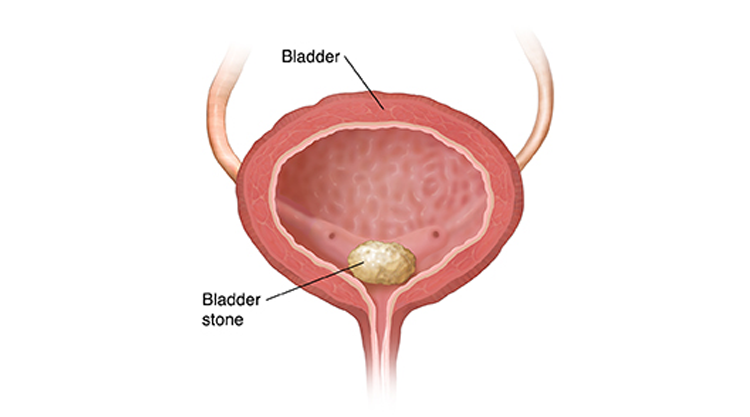
Urinary bladder stones, also known as vesical or cystic stones, are mineral masses that form in the bladder, often as a result of incomplete bladder emptying or concentrated urine. These stones can cause discomfort and lead to complications if left untreated. In this guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for bladder stones, with expert insights from Dr. Prabhat Ranjan, a distinguished urologist specializing in urinary disorders.
Bladder stones, or vesical stones, typically cause discomfort and urinary disturbances. A common symptom is pain or pressure in the lower abdomen, which worsens during urination or when the bladder is full. Painful urination, described as a burning or stinging sensation, is another frequent complaint.
Many individuals experience urinary urgency and frequency, often passing only small amounts of urine at a time. Difficulty initiating urination or a weak, interrupted flow can also occur. Blood in the urine (hematuria) may give it a pink, red, or brownish hue.
In some cases, stones irritate the bladder lining, causing cloudy or foul-smelling urine. Severe obstructions may lead to urinary retention, creating a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying. If untreated, bladder stones can cause recurrent urinary tract infections, bladder outlet obstruction, or kidney damage. Prompt medical attention is crucial to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Urology is a specialized field focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract disorders in both men and women, as well as conditions affecting the male reproductive system. A urologist’s expertise encompasses a wide range of issues, including kidney stones, bladder disorders, urinary infections, and prostate conditions.
Renowned urologists, like Dr. Prabhat Ranjan, bring advanced skills in managing complex cases, from minimally invasive surgeries to personalized medical therapies. With a patient-centric approach, they aim to provide accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and preventive care, ensuring optimal urinary health and improved quality of life for patients.
Treatment strategies depend on the size and symptoms of the bladder stones. Options include:
We're always here to assist you! Feel free to reach out with any questions, feedback, or inquiries about our services. Contact us today to see how we can help!

 Call Now Button
Call Now Button