- Delhi, NCR
- +91-7840059590
Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate hyperplasia, is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that often affects men as they age. Dr. Prabhat Ranjan, a leading urologist, provides essential insights into understanding, diagnosing, and treating BPH for better prostate health.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) primarily affects urinary function due to the enlarged prostate pressing on the urethra and bladder. Common symptoms include increased frequency of urination, especially at night (nocturia), and a persistent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is not full. Difficulty starting urination (hesitancy) is a frequent complaint, often accompanied by a weak or interrupted urine stream.
Many individuals experience a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, leading to repeated trips to the bathroom. Dribbling of urine after finishing and straining to urinate are other common symptoms. In some cases, urinary retention, the inability to empty the bladder, may occur, leading to discomfort and a risk of infection.
Over time, untreated BPH can result in complications such as bladder stones, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), or kidney damage. Early diagnosis and management can alleviate symptoms and prevent further health issues.
Dr. Ranjan recommends comprehensive diagnostic methods:
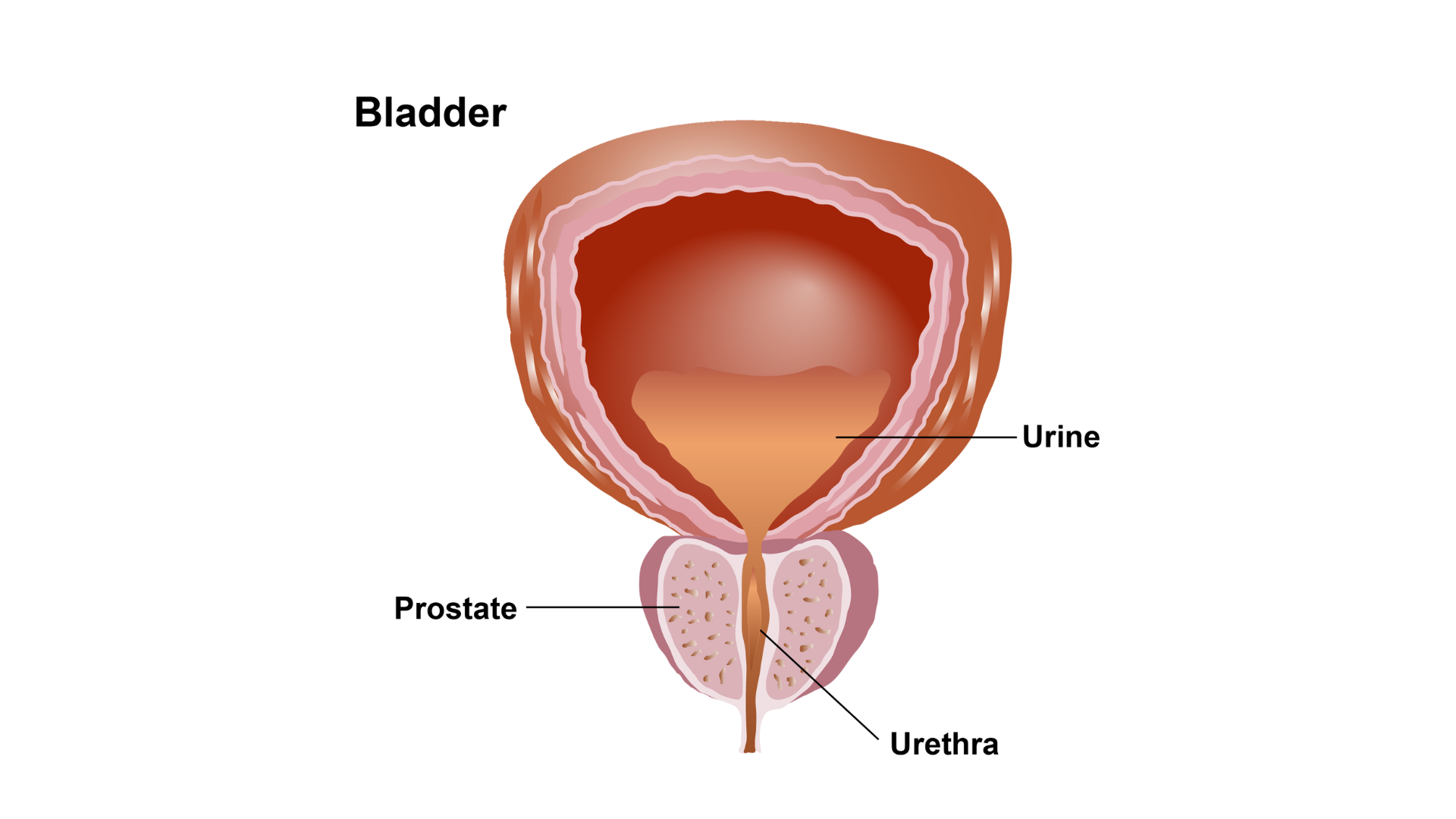
Dr. Ranjan tailored approach ensures effective symptom relief and quality-of-life improvement.
We're always here to assist you! Feel free to reach out with any questions, feedback, or inquiries about our services. Contact us today to see how we can help!

 Call Now Button
Call Now Button