- Delhi, NCR
- +91-7840059590
Pelvi-Ureteric Junction Obstruction (PUJO) is a condition where the flow of urine from the renal pelvis to the ureter is partially or completely blocked, leading to kidney damage if untreated. Dr. Prabhat Ranjan, a renowned urologist, shares valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for PUJO.
Pelvi-Ureteric Junction Obstruction (PUJO) presents with symptoms caused by impaired urine flow from the kidney to the ureter. Common symptoms include intermittent or persistent flank pain, often worsening after fluid intake. Patients may experience nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort due to increased pressure in the kidney. Hematuria (blood in urine) can occur, giving the urine a reddish or pinkish tint.
In severe cases, an abdominal mass may be palpable, and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common due to stagnant urine. Untreated PUJO can lead to complications such as kidney stones, hydronephrosis, or progressive loss of kidney function.
Dr. Ranjan emphasizes accurate diagnostic methods:
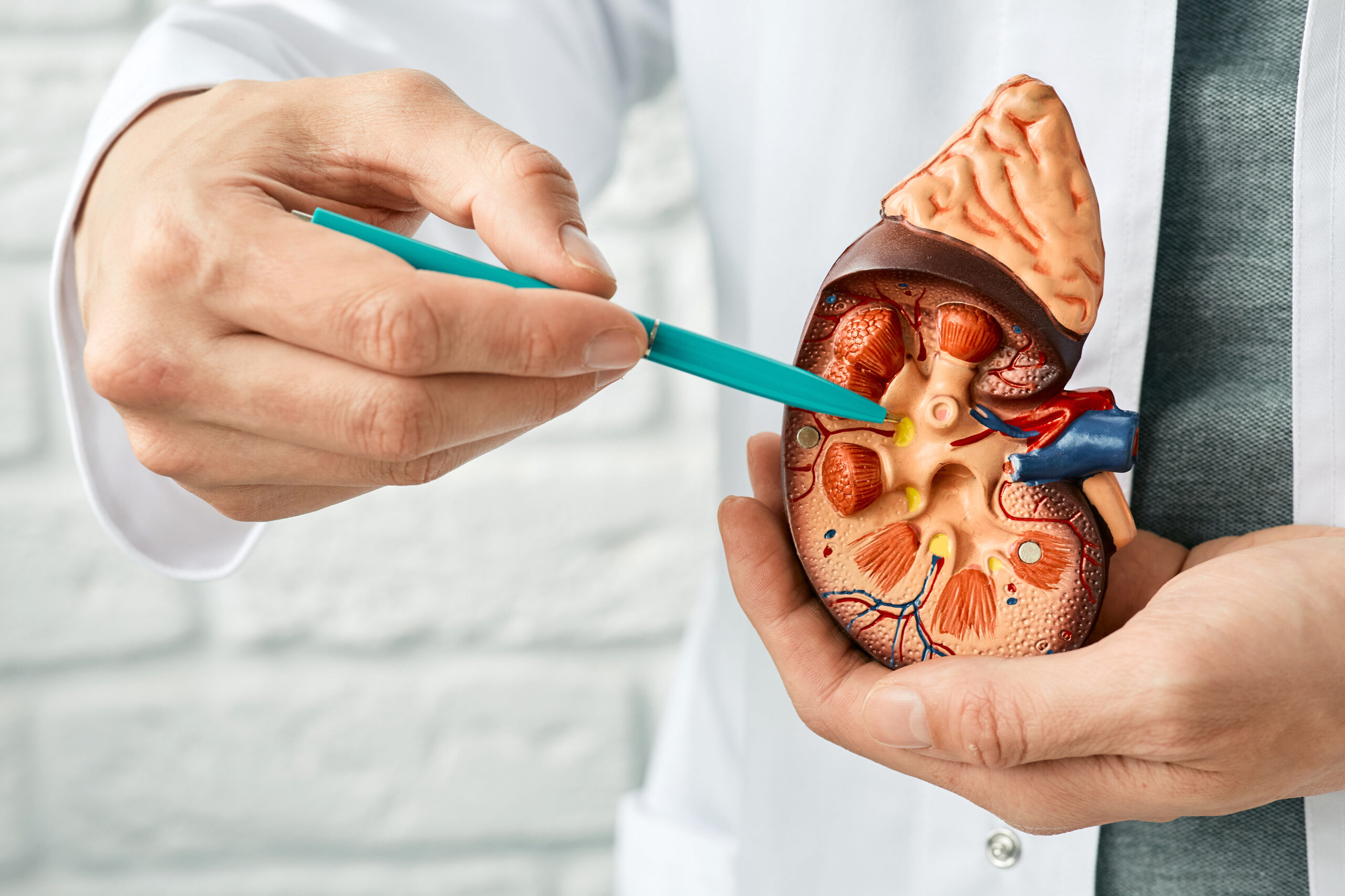
Dr. Ranjan tailors treatment plans to the severity of obstruction and patient needs.
While PUJO is often congenital, maintaining kidney health can prevent complications. Dr. Ranjan advises:
 Call Now Button
Call Now Button